
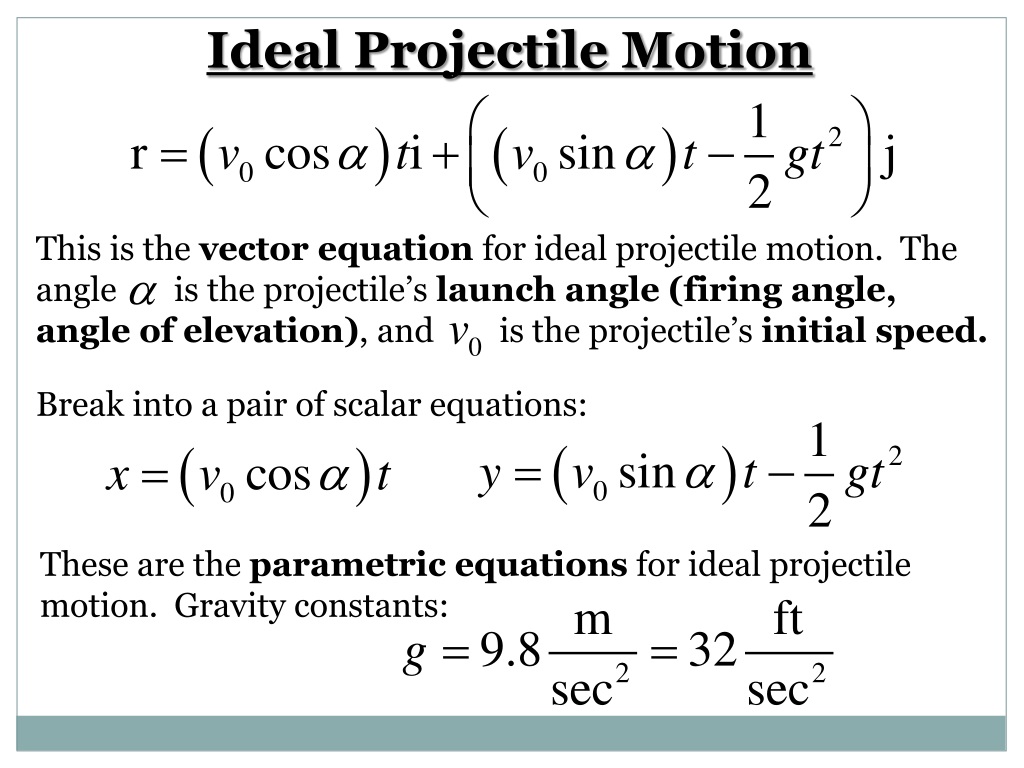
Check out StudyPug's tips & tricks on Projectile motion for Physics. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted … Projectile motion | StudyPug. About Transcript Using the equations of motion to figure out things about falling objects. projectile-motion-formula-t Projectile motion (part 1) (video) | Khan Academy. Using the displacement formula we can calculate the position ((x,y) coordinates) of a projectile at any given time. The trajectory of a projectile launched from ground is given by the equation y = -0.025 x 2 + 0.5 x, where x and y are the coordinate of the projectile on a . The maximum height of the projectile is given by … Projectile Problems with Solutions and Explanations. If v is the initial velocity, g = acceleration due to gravity and H = maximum height in metres, θ = angle of the initial velocity from the horizontal plane (radians or degrees). you know when to use distance vs displacement when dealing with projectiles? Projectile Motion - Definition, Formula, Examples, …. Using the equations of motion to figure out things about falling objects. Projectile motion (part 1) (video) - Khan Academy. We will answer all the usual questions that arise in a first year physics class regarding this motion. Please don't forget to leave a like if you found this helpful!Projectile motion/2D suvat: . Newton's Equations of Motion - A-level & GCSE Physics. We can use the displacement equations in the x and y . The equation for the magnitude of the displacement is Δr=√x2+y2.
Projectile motion problems are kinematics problems in 2 . However, at this level of physics, air resistance, also called "drag," will always be ignored. Projectile motion problems, or problems of an object launched in both the x- and y- directions, can be analyzed using the physics you already know. The horizontal and vertical motions may be separated and described by the general motion equations for constant acceleration. How far forward does it go before hitting the ground? (Assume that air resistance is negligible.) Solution Trajectories. 1 A projectile is launched with a velocity of 11m / s at an angle of 28 ∘ above the horizontal over flat level ground from a height of 2.0m above ground level. The vertical component, usinθ, accelerates due to . If u is the initial velocity at some angle θ, the horizontal component of the velocity, ucosθ, is constant.

The final vertical velocity is given by the following equation: vy= . Projectile motion questions are common in A-level physics as they combine the idea of resolving vectors into their components and using the equations of .
Ib projectile motion equations how to#
Horizontal and Vertical Displacement Initial Velocity Components Horizontally Launched Projectile Problems Non-Horizontally Launched Projectile Problems In Unit 1 of the … How to solve horizontally-launched projectile motion. What is a Projectile? - The Physics Classroom. Each kinematic equation serves a special purpose and aids in calculating different aspects of . These equations are called Kinematic Equations. How to Calculate a Projectile Motion - Video & Lesson. 0.40 m away from it, what must be the horizontal velocity of giraffes as they leave the conveyor . 0.60 m below the level of the conveyor belt and. Section 1 Projectile Motion: Practice Problems. URGENT: What equations ARE NOT on the AQA GCSE Physics equation sheet? AQA AS level physics 2021 paper 2(MECHANICS) These equations can only be applied to the . The laws of constant acceleration can be used to derive the horizontal and vertical components of a projectile. Projectile Motion Sports Science Degree Physical Education. Since there is no horizontal force at work in . An object that moves under gravity in the air is a projectile. In this tutorial, you will learn the following. Projectile motion equations a level physicsProjectile Motion for A Level Physics and Mechanics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
